Understanding Foley Catheters
What is a Foley Catheter?
A Foley catheter is a medical device utilized for urinary drainage, commonly employed in hospitals and other healthcare environments. This flexible tube is gently inserted into the bladder via the urethra, facilitating the direct collection of urine into a bag. The catheter features a small balloon at its tip, which is inflated once it reaches the bladder to secure the catheter’s position.
Common Uses of Foley Catheters
Foley catheters are commonly used in various medical scenarios. They are often employed during surgeries to manage urinary drainage and ensure that the bladder remains empty. They are also utilized in patients who are unable to urinate due to medical conditions such as urinary retention, spinal cord injuries, or certain types of surgeries. Additionally, foley catheters are utilized in palliative care to provide comfort to patients by managing urinary elimination without the need for frequent movement.
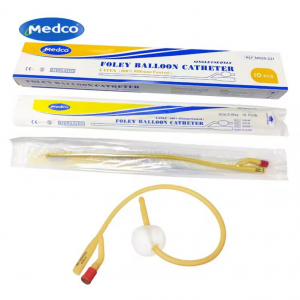
Anatomy of a Foley Catheter
A foley catheter generally consists of three main parts: the catheter tube, the balloon, and the drainage bag. The catheter tube is the long, flexible tube that is inserted into the bladder. The balloon, located near the tip of the catheter, is inflated to keep the catheter securely within the bladder. This balloon is filled through a valve on the outside end of the catheter.The external section of the catheter connects to a drainage bag where urine is collected. Latex foley catheters are commonly used in medical settings for their flexibility and durability. They are made from latex or silicone materials to ensure these qualities.
Common Problems Associated with Foley Catheters
Infections and How They Occur
Infections are a prevalent issue related to foley catheters. Catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) are common because the urinary catheter can introduce bacteria into the bladder. This can happen during the insertion process or through the catheter’s external surface where bacteria may ascend into the urinary tract. Preventing CAUTIs involves strict adherence to aseptic techniques during insertion and routine catheter care. It’s crucial to regularly clean the insertion site and maintain a closed drainage system to minimize infection risks.
Discomfort and Pain Issues
Numerous patients encounter discomfort and pain when using a Foley catheter. This unease often arises from the catheter’s physical presence in the urethra and bladder. In certain instances, the processes of insertion or removal can lead to pain and irritation. Applying proper lubrication during insertion, selecting the correct catheter size, and handling it with care can mitigate these problems. Conducting regular assessments and obtaining patient feedback can assist in adjusting the catheter placement to alleviate discomfort.
Blockages and Obstructions
Blockages are another frequent issue with foley catheters. These blockages can occur due to blood clots, sediment, or crystal build-up within the catheter, which prevents urine from draining properly. To minimize this problem, healthcare providers may recommend adequate hydration to the patients and perform regular checks on the catheter and drainage system. Flushing the catheter periodically can also help in removing blockages and ensuring smooth urine flow.
Leakage and Malfunctions
Leakage around the foley catheter can occur due to various reasons such as an inappropriate catheter size, the balloon not being properly inflated, or the catheter shifting from its original position. Malfunctions may occur if the catheter material deteriorates or due to mechanical issues with the drainage system. To address this, it is important to use the correct catheter size, regularly check the balloon inflation, and ensure that the catheter and the attached drainage system are functioning properly. Routine checks and maintenance can prevent leakage and inform timely replacements if the catheter is damaged or malfunctioning.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Preventing Infections
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Proper cleaning and maintenance are paramount for preventing infections associated with a foley catheter. Daily cleaning of the catheter insertion site with mild soap and water is recommended to remove any potential contaminants. Cleaning should be gentle to avoid irritation.Ensuring the urine bag and catheter are kept clean can significantly reduce the chances of infection. Proper hygiene extends to handwashing before and after handling the catheter, as well as regularly cleaning and disinfecting the drainage bag and tubing.
Proper Sanitization Techniques
Employing proper sanitization methods is essential when managing a Foley catheter. Wearing disposable gloves during catheter care helps to prevent bacterial contamination. Additionally, disinfecting the catheter and its drainage system with recommended antiseptics reduces the risk of infections. Regularly sanitizing the catheter tubing, particularly after emptying the drainage bag, is vital for maintaining a sterile environment. This stringent sanitization protocol is crucial in preventing infections.
Managing Discomfort and Pain
Correct Insertion Techniques
Utilizing the right insertion techniques can significantly mitigate discomfort associated with a foley catheter. Health professionals should follow precise methods for sterile insertion to minimize trauma. The use of gentle techniques and ensuring the patient is in a relaxed state help reduce discomfort. Additionally, medical practitioners should be trained and well-versed in insertion procedures to ensure patient comfort and reduce the likelihood of pain during the process.
Use of Lubricants and Pain Relievers
Applying lubricants during the insertion of a foley catheter can greatly alleviate discomfort. Lubrication reduces friction, helping the catheter slide into the urethra smoothly. For patients experiencing pain, topical anesthetics or pain relievers may be utilized under medical guidance. Continuous monitoring and asking patients to report any discomfort can lead to prompt management with appropriate pain relief measures, thus ensuring a more comfortable experience.
Addressing Blockages
Flushing the Catheter Properly
Flushing a foley catheter periodically can help prevent blockages caused by sediment or blood clots. This procedure should be performed by trained healthcare providers using sterile techniques to avoid introducing infections. By flushing the catheter, any buildup within the tube can be dispersed, ensuring a clear path for urine drainage. Different from medical disposables, regular flushing schedules should be adhered to as part of routine catheter maintenance.
Ensuring Adequate Hydration
Ensuring proper hydration is crucial to avoid blockages in a foley catheter. Patients should be encouraged to drink an adequate amount of fluids each day unless advised otherwise by a medical professional. Staying well-hydrated helps to dilute the urine, thereby minimizing the risk of crystal formation and subsequent blockages. This practice not only aids in keeping the catheter clear but also supports overall urinary tract health by reducing the chances of sediment formation.
Preventing Leakage and Malfunction
Appropriate Sizing and Fit
Choosing the appropriate size and fit of a foley catheter is crucial in preventing leakage and ensuring effective urinary drainage. An improperly sized catheter can lead to discomfort and frequent leakage around the insertion site. Healthcare providers should assess the patient’s anatomy to select the correct catheter size. Additionally, periodic re-evaluation of the catheter’s fit is necessary to ensure it remains appropriate over time.
Timely Inspection and Replacement
Regular inspection and timely replacement of a foley catheter can preempt potential malfunctions. Routine checks should be conducted to ensure that the catheter and drainage system are intact and functioning properly. If any signs of wear, tear, or mechanical issues are detected, immediate replacement is warranted. A scheduled replacement protocol minimizes the risk of malfunctions, and timely interventions can maintain effective and trouble-free catheter usage.
Future Developments in Foley Catheter Usage
Innovations in Design and Material
Innovations in Design and Material have revolutionized the field of medical devices. One such example is the Rehabilitation Appliance, which has greatly improved the quality of life for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. This innovative device incorporates advanced materials and ergonomic design to provide optimal support and assistance during the rehabilitation process. Another breakthrough in the field of medical devices is the Skin Rejuvenation Device. This cutting-edge device utilizes state-of-the-art technology to stimulate collagen production and improve skin elasticity. With its sleek design and user-friendly interface, the Skin Rejuvenation Device offers a convenient and effective solution for individuals seeking to enhance their skin’s appearance.
Additionally, innovations in design and material have also transformed the Foley Catheter, a commonly used medical device for urinary drainage. The use of high-quality materials and improved design features has made the Foley Catheter more comfortable and less prone to complications, ensuring better patient outcomes. These examples highlight the significant impact that innovations in design and material have had on the development of medical devices. By continuously pushing the boundaries of technology and incorporating user-centric design principles, these devices are not only more effective but also more comfortable and convenient for patients.
The future of foley catheter usage is set to benefit from innovations in design and materials. Modern advancements are focusing on creating more patient-friendly designs that enhance comfort and reduce complications. Scientists and medical device manufacturers are working on developing catheters made from biocompatible materials that minimize irritation and inflammation. Silicone and hydrophilic coatings are among the materials being explored to reduce friction during insertion and minimize bacterial adherence, such as Medco’ s medical silicone coated 2 way latex foley catheter. Additionally, smarter designs with integrated sensors could potentially monitor urine flow and detect blockages or leakage, thereby providing real-time feedback to healthcare providers and improving patient outcomes.
Advances in Infection Control Technologies

The risk of infection associated with foley catheter use is a significant concern, prompting the development of new infection control technologies. Innovations include the use of antimicrobial coatings on catheters that prevent bacterial colonization. These coatings can be infused with silver ions, antibiotics, or other antimicrobial agents to actively combat the growth of bacteria on the catheter surface. Furthermore, advancements in closed drainage systems reduce the risk of infection by maintaining a sterile environment during urine collection. Emerging technologies, such as ultraviolet (UV) light sanitation systems, are being integrated to disinfect the catheter and drainage system regularly, enhancing overall infection control measures. The future of foley catheter usage looks promising with these advances, potentially leading to safer and more effective urinary drainage solutions. The concern over infections linked to foley catheter use has led to the creation of advanced infection control methods.
One such innovation is the application of antimicrobial coatings on catheters to inhibit bacterial colonization. These coatings may contain silver ions, antibiotics, or other antimicrobial substances that work actively to prevent bacterial growth on the catheter’s surface. Additionally, improvements in closed drainage systems help minimize infection risks by ensuring a sterile environment for urine collection. New technologies like UV light sanitation systems are being incorporated to regularly disinfect both the catheter and its drainage system, thereby boosting overall infection control protocols. With these technological advancements, the future use of foley catheters appears to be moving towards safer and more efficient urinary drainage options.