Understanding Medical Sutures for Surgery and Their Characteristics
Definition and Purpose of Medical Sutures
Surgical sutures help to add to the work of medicine by holding tissue in place during or after operation or trauma for facilitating efficient healing while reducing possibilities of infection in the area and therefore offering better outcomes to tissue repair. The major function is to promote tissue healing without jeopardizing integrity in the same location.
Key Characteristics of Surgical Sutures
Several properties and forms decide the functions in choosing how suitable surgical sutures are for particular procedures. Tensile strength is significant in that it enables the suture to resist the tension encountered during healing. Flexibility is significant in enabling the suture to conform to tissue movement without injury. Ensuring knot security is essential to prevent any slipping and maintain wound closure. The absorption rate is another factor to consider for absorbable sutures that break down gradually in the body.
Classification and Materials of Medical Sutures
Types of Medical Sutures
Different types can categorize sutures by their design and purpose. Single strand monofilament sutures allow for movement through tissues and reduce the riskof infection.Multi strand multifilament sutures offer increased strength. May raise infection risks due to their braided composition. The other classification is based on whether they are absorbable or not—absorbable sutures break down naturally in the body over time whereas non absorbable ones stay intact unless taken out.
Materials Used in Surgical Sutures
Natural Materials
Surgical sutures made from materials like silk and catgut are commonly used in medical procedures. Silk is favored for its ease in handling and secure knots. May lead to tissue reactions because it is organic. Cat gut is sourced from animal intestines and is used for sutures; however its usage has diminished in favor of synthetic options due to inconsistent absorption rates and the risk of tissue reactions.
Synthetic Materials
Artificial materials have gained popularity for their performance and lower chances of causing negative responses in recent times. Commonly known as synthetic materials including polyglycolic acid (PGA) polylactic acid (PLA) and polypropylene are predominantly used based on their level of absorption good tensile strength and minimal reactivity against tissue. In addition, they also possess the flexibility of being used to create non-absorbable forms which may be designed according to a specific surgical requirement.
Key Factors in Choosing Medical Sutures
Considerations for Different Surgical Procedures
In the world of medicine picking the kind of suture is key depending on the surgical procedure at hand. For example heart surgeries need sutures that are strong and gentle on tissues to keep blood vessels intact. On the hand plastic surgeries may opt for delicate monofilament sutures to reduce scarring. When it comes to procedures tough non absorbable sutures are essential to endure the strain during healing.
Patient-Specific Factors in Suture Selection
Patient specific factors are significant in the choice of sutures. There are factors like the patient’s age and health status. Both can affect their tolerance of suture material based on their history of previous medical conditions.
Evaluating Suture Strength and Durability
Ensuring the tensile strength and longevity of the sutures is essential to wound closure and healing that includes determining the tensile strength necessary for every case and how long the suture should be left in the tissue before it gets absorbed or can be taken out. Determining these factors’ decision-making should be counterbalanced by others like ease of use and knot security for enhanced patient outcomes.
With knowledge of these aspects of surgical sutures—from definition and characteristics to classification and material composition—medical professionals can make informed decisions when selecting the best medical suture for each unique surgical case. This offers the optimum healing conditions and minimizes wound closure-related complications.
Applications of Medical Sutures in Surgery
Common Surgical Procedures Utilizing Sutures
During types of surgical procedures such as those involving the abdomen or heart surgeries for example, sutures are vital for closing incisions and mending tissues inside the body that have undergone surgery Sutures are necessary in cardiovascular surgeries to mend blood vessels and heart tissues to prevent any leaks and ensure proper blood circulation Orthopedic surgeries often use sutures to attach tendons and ligaments as well as secure bone grafts Plastic and cosmetic surgeries use stitches to carefully close wounds for minimal scarring and better aesthetic results.
Techniques for Suture Application
Knotting Techniques
Masterful skills in tying knots play a role in guaranteeing the stability and safety of surgical stitches used by surgeons in their practice. Surgeons tie the suture material securely in place either using knots or surgeons knots. Square knots involve tying two overhand knots in succession so that the tension is maintained without slipping. Conversely, surgeons’ knots incorporate an additional twist on the initial loop to contribute to the security and stability of the knot, especially with slippery suture material or compressive tissues. Proficiency in these knotting techniques is paramount to wound closure and healing process security.
Stitching Methods
Different sewing techniques are used based on the type. Complexity of the surgery and tissue involved. Certain principles apply to each approach and impact results in different ways. Intermittent sutures are formed by placing stitches in a line along the incision and tying each one separately. This allows for adjustment of tension at different points but takes time. In contrast, a continuous suture is when one thread is run along the incision line which allows for faster closure and even distribution of tension. A subcuticular suturing is a special technique in which sutures are inserted in the dermis layer. This approach yields pleasing outcomes while minimizing surface scarring.
Introduction to Medco: Reasons and Advantages for Purchasing Their Medical Sutures
Overview of Medco as a Company
Medco is a medical device company with expertise in specialized medical products such as high-grade surgical sutures. With long years of history in the health sector, Medco has found itself as an organization that produces cutting-edge medical products aimed at meeting the requirements. Their effort to improve technology is reflected in their intensive research and development functions.
Benefits of Choosing Medco’s Medical Sutures
Quality Assurance and Standards
Medco puts importance on ensuring the quality and reliability standards. Because their medical sutures are met through thorough testing procedures in compliance with industry regulations.
Range of Products Available
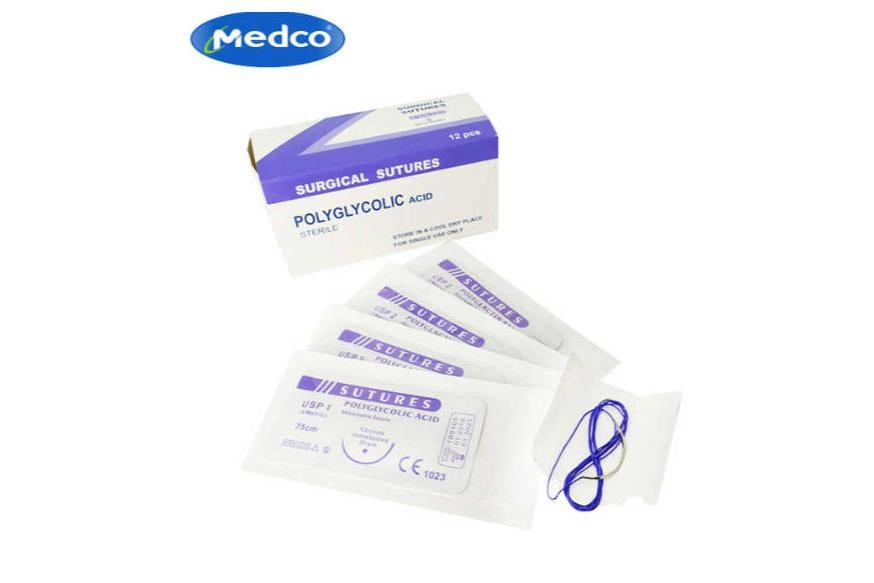
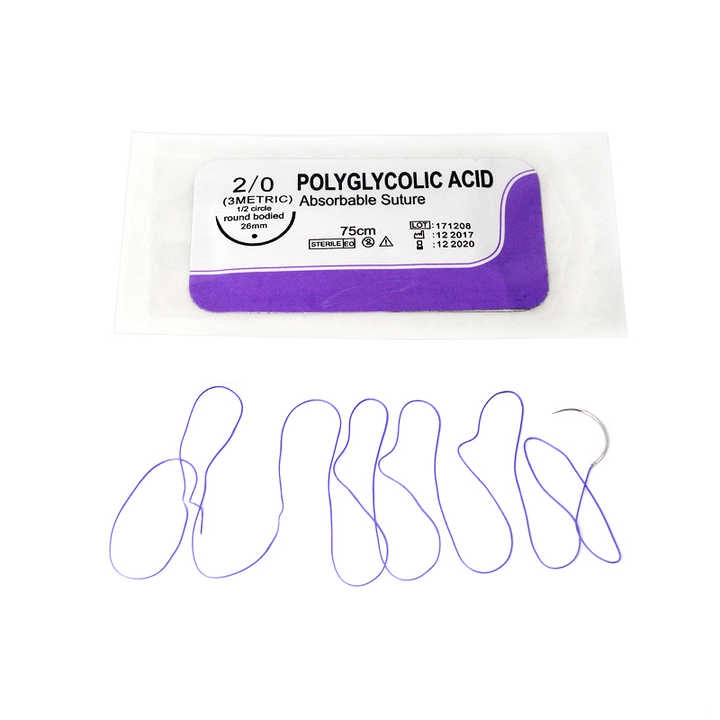
Medco provides a selection of surgical sutures tailored to meet various surgical requirements. It offers both absorbable and non absorbable options. The options are crafted from different materials like polyglycolic acid (PGA), polydioxanone (PDO) and polypropylene in their product lineup. Those materials enable medical professionals to choose the most suitable suture for specific procedural needs and patient factors.
Medco offers more than typical sutures. They also provide unique products like antimicrobial coated sutures to lower the chances of infection during surgery. These special choices demonstrate Medco’s dedication to tackling changing healthcare obstacles with solutions.
When surgeons opt for Medco’s sutures, they can trust in using products that blend advanced technology with established dependability—ultimately elevating patient care by enhancing wound healing processes.
FAQ
Q: What type of suture is used in surgery?
A: Surgeons usually opt for either polypropylene or polydioxanone sutures when repairing fascia based on the required strength level.
Q: What is the difference between medical stitches and sutures?
A: While stitches and sutures are often thought to be terms by many peoples standards; in the medical field they actually hold distinct meanings. Sutures are the threads or strands utilized to seal off wounds while stitches pertain to the physical action involved in closing the wound up.